Products
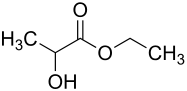
Ethyl lactate
Ethyl lactate, lactic acid ethyl ester or 2-hydroxypropanoic acid ethyl ester is the chemical compound of lactic acid with ethanol in the form of an ester. Depending on its synthesis, the substance is available as racemate or pure substance.
If ethyl lactate is split back into its starting materials ethanol and lactic acid (e.g. by a chemical reaction), it can be decomposed in nature. Esterases, naturally occurring enzymes, can also carry out the split back into the original materials. Lactic acid ethyl ester is therefore considered a "green solvent", as it does not leave any toxic decomposition products in the ecosystem. This provides an advantage over chlorinated solvents or glycols or glycol ethers, which have a higher biological toxicity.
In this product area, we work together with the European manufacturers Corbion / Purac (Purasolv ®) and Galactic (Galaster ™), among others.
1. Production
The substance can be produced by technical or biotechnological means. In technical synthesis, pure lactic acid (obtained from petrochemical processes) is usually cooked in an excess of ethanol until esterification takes place. The process is not stereoselective, which is why a racemate is formed. The resulting products, such as water, must be further removed until the pure substance ethyl lactate is obtained.
If ethyl lactate is produced biologically, it is done with the help of bacteria and microorganisms. The starting material is usually a product containing starch, such as corn, which is processed into lactic acid with the help of bacteria via glucose. Another type of bacteria processes starch into ethanol. After several purifications, the two substances ethanol and lactic acid, each in diluted form, are fed to another microorganism. This microorganism esterifies the two substances with the help of enzymes to form the final product. As in all biological synthesis processes, the biomass must now be centrifuged and the obtained substance purified. Thanks to the stereoselective property of the enzymes contained in the process, no racemate is obtained.
2. Use/effect
Ethyl lactate has the following positive physico-chemical properties: excellent solubility for resins (nitrocellulose, alkyds, etc.), relatively high solubility in water, good solubility in organic solvents, low volatility and a relatively high boiling point (154 degrees Celsius). Combined with its low biological toxicity, ethyl lactate is therefore suitable as a solvent, co-solvent, cleaning, degreasing and mordant agent. Applications can be found in the metal, automotive, aerospace, paint, ink, resin and coating industries, as well as in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and semiconductor industries.
Due to its low toxicity, the lactic acid ethyl ester is also used in the beverage and food industry: here it serves as an aroma or fragrance in wine or various fruits.
3. Further properties/facts
Even if the boiling point is 154 degrees Celsius, flammable vapour-air mixtures can form even above 46 degrees Celsius. This property requires special storage and controlled processing.
Newer manufacturing processes are increasingly focusing on biological synthesis. The advantages are milder process temperatures with lower energy and disposal costs, and the use of biological starting material. New bacterial species and improved reaction processes are expected to lead to more efficient production processes and higher yields.
Product details
| Qualities: | 99,5 % FCC, 98 % technical |
|---|---|
| CAS number: | 687-47-8/97-64-3/141-78-6 |
| EG number: | 211-694-1/202-598-0 |
| Origin country: | Belgium, Netherlands, Japan |
| Physical state: | liquid |
| Container: | drums |
| INCI: | Ethyl lactate |
| EINECS: | 607-022-00-5 |
| Durability: | 24 months |
| Storage: | should be stored at a cool, dry and light shielded place |
More Products
Your contact

Manuel Bahr

Christine Ademes